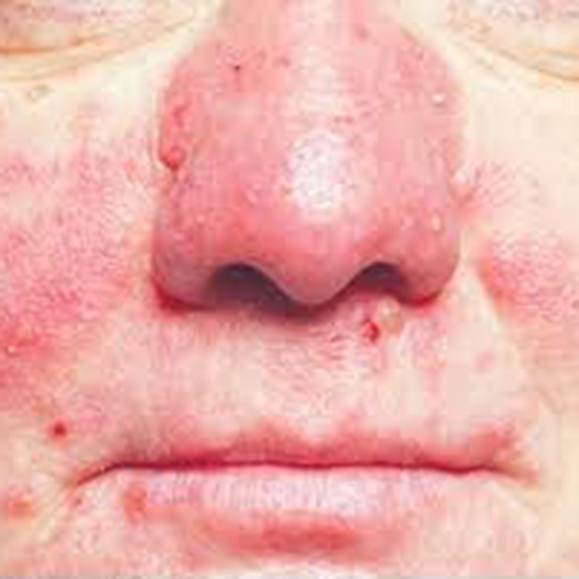
Rosacea
Home • Dermatology • Common Skin Conditions • RosaceaAbout
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition primarily affecting the face. It typically manifests as redness on the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. Over time, the redness may become more persistent, and blood vessels may become visible. In some cases, rosacea may also involve acne-like breakouts and could thicken the skin on the nose
AboutSymptoms
- Persistent redness resembling a blush or sunburn
- Visible blood vessels on the face
- Acne-like breakouts and very oily skin
- Skin sensitivity, which may include burning or stinging sensations
- In more advanced cases, skin thickening, often around the nose (a condition known as rhinophyma)
- Eye irritation in some individuals, which can manifest as red, irritated, and swollen eyes and eyelids
Causes
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but it may involve a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. Potential causes and contributing factors include:
- Immune system reactions
- Vascular irregularities
- Presence and density of skin mites (such as Demodex folliculorum)
- H. pylori bacteria
- Exposure to sunlight
- Stress
- Spicy foods, alcohol, and temperature extremes which may aggravate the condition.
Treatments
Managing rosacea typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments to control and reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
Medical Treatments
- Topical Medications: These are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation and redness. Commonly prescribed topical agents include metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin.
- Oral Antibiotics: For moderate to severe rosacea, oral antibiotics like doxycycline or minocycline may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and clear up acne-like lesions.
- Isotretinoin: In severe cases, especially those resistant to other treatments, isotretinoin may be used as a potent option to treat rosacea.
Laser Therapy
- Laser Therapy: Treatments like intense pulsed light or BroadBand Light can be effective in reducing redness, removing visible blood vessels, and improving the overall appearance of the skin. These treatments work by targeting and collapsing the dilated blood vessels responsible for the redness.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Skin Care: Using gentle skin care products that do not aggravate the skin is crucial. Non-irritating, fragrance-free products are recommended. Sun protection with broad-spectrum sunscreen that has an SPF of 30 or higher is essential to protect sensitive skin and prevent flare-ups.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is a critical aspect of managing rosacea. Common triggers include hot foods, alcoholic beverages, extreme temperatures, and stress.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some patients might find it helpful to avoid spicy foods and hot drinks, which can exacerbate symptoms.