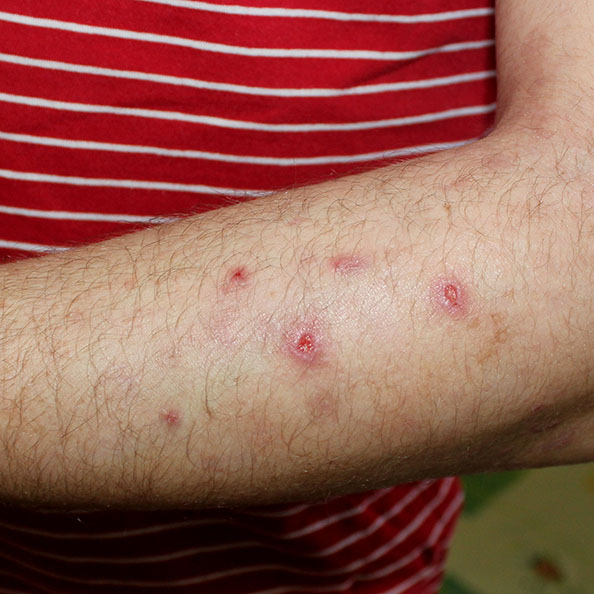
Prurigo nodularis
Home • Dermatology • Common Skin Conditions • Prurigo nodularisSymptoms
- Itchy bumps on the skin that can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the arms and legs.
- Nodules are usually red, pink, skin-colored, or brownish.
- The affected areas may be covered with crusts or scales due to repeated scratching.
Causes
The exact cause of Prurigo Nodularis is not fully understood. It is often associated with other skin conditions that cause itchiness, such as atopic dermatitis, or systemic conditions like end-stage kidney disease. Some people develop prurigo nodularis without any apparent underlying condition.
CausesTreatments
Treating prurigo nodularis involves addressing both the nodules and the itchiness to improve the quality of life and skin condition:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itch. Calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can also be effective, especially in sensitive areas where steroids are less desirable.
- Systemic Treatments: For severe cases, systemic medications like corticosteroids, gabapentin, or even immunosuppressants may be prescribed. Dupixent is an FDA-approved treatment that has given remarkable relief to those who suffer with prurigo nodularis. Dupixent is a biologic medication that works by inhibiting the signaling interleukins that drive the type of inflammation commonly seen in prurigo nodularis.
- Phototherapy: UVB phototherapy has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms by suppressing the immune response in the skin.
- Antihistamines: These can help manage the itch, especially sedating antihistamines at night to reduce scratching during sleep.
- Emollients and Moisturizers: Regular use of these can help soothe the skin and reduce dryness, which may alleviate some of the itchiness.
Self-Care
- Avoid Scratching: Keeping fingernails short and wearing gloves at night might help reduce skin damage from scratching.
- Skin Care: Using mild soaps and applying moisturizers frequently can help maintain skin integrity.
- Stress Management: Since stress can exacerbate itching, techniques like relaxation therapy, mindfulness, or counseling might be beneficial.
When to See a Doctor?
It’s important to consult a dermatologist if:
- The itching disrupts sleep or daily activities.
- The skin changes are severe and widespread.
- Over-the-counter remedies do not relieve symptoms.