Melasma
Home • Dermatology • Common Skin Conditions • MelasmaSymptoms
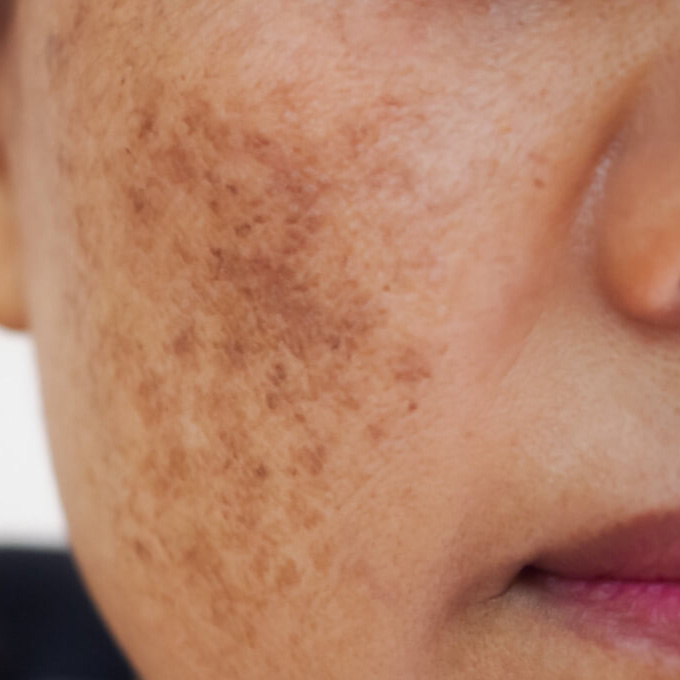
Melasma appears as darker-than-normal patches that develop gradually and produce a mottled pigmentation that is darker than the surrounding skin. These patches are symmetrical, with matching marks on both sides of the face.
SymptomsCauses
The exact cause of melasma is unknown, but it typically occurs when the melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigments in the skin, produce too much color. Factors that may trigger melasma include:
- Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light stimulates melanocytes, which can lead to melasma.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnant women often experience melasma due to hormonal changes, sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy.” Birth control pills and hormone therapy can also trigger melasma.
- Cosmetics: Skin products that irritate the skin may worsen melasma.
Treatments
The treatment of melasma requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on both reducing visible pigmentation and preventing further darkening. Here’s a deeper look at the various treatment options available for managing melasma effectively:
- Topical Agents
-
- Hydroquinone: This is the most commonly prescribed medication for melasma. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Hydroquinone is available in various strengths, with higher concentrations available through a prescription.
- Tretinoin and Other Retinoids: These compounds help to accelerate cellular turnover, which can fade dark spots over time.
- Triple Combination Creams: These creams combine hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a corticosteroid, providing a potent treatment for melasma that addresses inflammation, pigmentation, and skin renewal.
- Chemical Peels – Peels can help by removing the upper layers of the skin, allowing new skin to surface. This process can also help lighten hyperpigmentation.
- Laser Treatments – Laser therapy can be an option for treating melasma. Procedures like fractional lasers work by targeting the deeper layers of the skin to break up pigmented cells. However, there is a risk that laser treatments can sometimes trigger more pigmentation, especially in darker skin tones.
- Sun Protection – Daily and rigorous sun protection is crucial in managing melasma. Broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher, wide-brimmed hats, and sun-avoidant behavior are necessary to prevent further pigmentation and worsening of existing patches.
- Oral Supplements – Some oral antioxidants such as tranexamic acid, polypodium leucotomos extract, and vitamins C and E might help in managing melasma by reducing oxidative stress that can trigger pigmentation.
- Microneedling – Microneedling, sometimes combined with topical treatments, can enhance the delivery of active ingredients deep into the skin, helping in the reduction of melasma.
Treatments