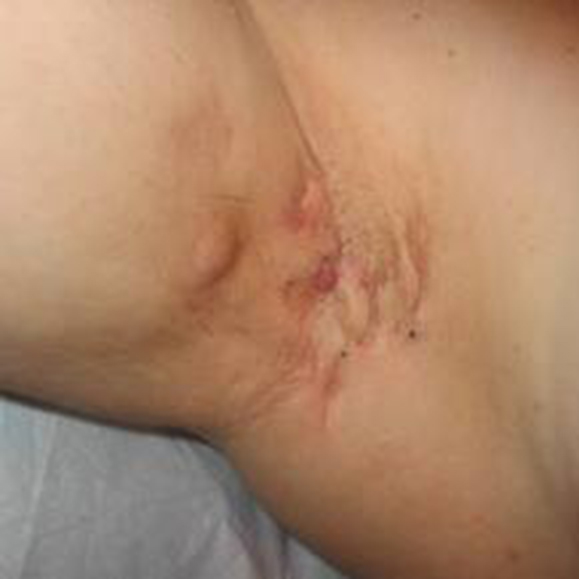
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Home • Dermatology • Common Skin Conditions • Hidradenitis suppurativaAbout
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the appearance of painful lumps under the skin. These lumps typically develop in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts. HS can cause a range of symptoms, including abscesses and scarring.
AboutSymptoms
HS usually presents with a combination of the following symptoms:
- Painful lumps beneath the skin that may persist or recur
- Deep-seated abscesses that can rupture and leak pus
- Sinus tracts or tunnels that can form under the skin, leading to scarring and chronic infection
- Significant discomfort and potential restrictions in movement due to pain and scar formation
Causes
The exact cause of HS is not fully understood, but it begins with clogging of hair follicles. Contributing factors include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of HS can increase the risk.
- Hormonal factors: Flare-ups may be connected with hormonal changes such as menstrual cycles.
- Smoking and obesity: These are known to exacerbate the condition and may trigger onset in predisposed individuals.
Treatments
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) treatment aims to manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and maintain quality of life. Here’s an expanded look at the various treatment options available for managing this challenging skin condition:
- Medications
-
- Antibiotics: Used both topically and orally to reduce inflammation and treat infections associated with HS. Long-term antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to prevent recurrent infections.
- Hormonal Therapies: Such as oral contraceptives or anti-androgen therapy (e.g., spironolactone) can be effective, particularly in women whose symptoms flare with their menstrual cycle.
- Biologic Drugs: Humira and Cosentyx are the only FDA-approved biologics for treating HS. They target cytokines involved in inflammation.
- Retinoids: Oral retinoids, like acitretin, are sometimes used for their ability to reduce keratin production, which can help in managing HS.
- Pain Management
-
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Injected directly into the lesions to quickly reduce swelling and pain.
- Surgical Options
-
- Incision and Drainage: While not a long-term solution, this can be used to relieve pain by draining large, painful abscesses.
- Excision: Removing the affected skin areas can be effective for severe cases. This can range from removing single lesions to extensive areas of skin, depending on the severity of the condition.
- CO2 Laser: This method vaporizes the affected tissue and is useful in managing HS by reducing the number of glandular structures that cause the disease.
- Lifestyle Modifications
-
- Weight Management: Losing weight can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms as reduced skin friction decreases the likelihood of new lesions.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a known trigger and worsening factor for HS. Quitting smoking can improve the course of the disease.
- Diet: Some patients report improvement with dietary changes, such as reducing dairy and brewer’s yeast.
Managing HS often requires a multi-disciplinary approach, including dermatologists, surgeons, and sometimes chronic pain specialists. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is crucial for adapting treatment plans as the condition progresses or improves.
Biologic medications have become an important option for managing moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), particularly when other treatments have failed to control the symptoms. Here’s an overview of how biologics work for HS and the types commonly used:
Treatments